Space research, a captivating and expansive field, involves scientific study conducted in outer space and through the observation of celestial phenomena. This domain not only fuels our curiosity about the universe but also drives technological advancements and enhances our understanding of various scientific disciplines. From Earth science to physics, space research encompasses a wide array of studies that have profound implications for life on Earth and beyond.
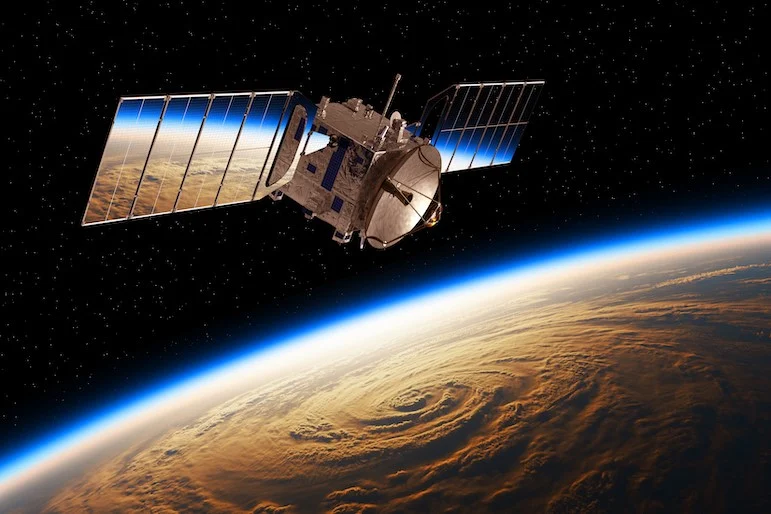
Space technology serves as the backbone of space research, enabling scientists to explore the cosmos and gather invaluable data. Satellites, telescopes, and spacecraft are pivotal tools that allow us to observe distant galaxies, monitor Earth’s climate, and even search for signs of extraterrestrial life. Innovations in space technology have led to significant breakthroughs, such as the Hubble Space Telescope’s breathtaking images of the universe and the Mars rovers’ exploration of the Red Planet’s surface.
These technologies not only advance our knowledge of space but also have practical applications on Earth. For instance, satellite technology is crucial for weather forecasting, global communications, and navigation systems, demonstrating how space research contributes to everyday life.
Space research is inherently interdisciplinary, drawing from and contributing to fields such as Earth science, materials science, biology, medicine, and physics. In Earth science, satellites provide critical data for studying climate change, natural disasters, and environmental conservation. By observing Earth from space, scientists can gain insights into atmospheric patterns, ocean currents, and land use changes, informing policies and strategies for sustainable development.
In biology and medicine, space research offers a unique perspective on human health and adaptation. Studying the effects of microgravity on the human body helps researchers understand bone density loss, muscle atrophy, and other physiological changes, providing valuable information for improving healthcare on Earth and preparing for long-duration space missions.
Physics, perhaps the most fundamental of sciences, finds a natural home in space research. Observations of cosmic phenomena, such as black holes, neutron stars, and cosmic microwave background radiation, challenge existing theories and inspire new ones, pushing the boundaries of our understanding of the universe.
The observable universe, a vast expanse filled with galaxies, stars, and planets, is the ultimate laboratory for space research. By studying this immense canvas, scientists seek answers to some of humanity’s most profound questions: How did the universe begin? Are we alone in the cosmos? What is the nature of dark matter and dark energy?
Telescopes like the James Webb Space Telescope, set to succeed Hubble, promise to unveil new secrets of the universe, offering unprecedented views of distant galaxies and the potential to discover habitable exoplanets. These explorations not only satisfy our innate curiosity but also inspire future generations to pursue careers in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM).
Space research is a testament to human ingenuity and the relentless pursuit of knowledge. By exploring the final frontier, we not only uncover the mysteries of the universe but also enhance our understanding of life on Earth. As we continue to push the boundaries of space exploration, the interdisciplinary nature of space research will undoubtedly lead to discoveries and innovations that benefit all of humanity. Whether through technological advancements or deeper insights into the cosmos, space research remains a vital and inspiring endeavor that shapes our future.